Y Altintas, MY Talpur, E Mutlugün – Optics Express, 2017
Abstract
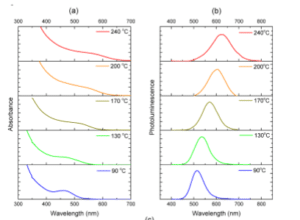
Semiconductor quantum dots have been on demand for niche optoelectronic applications providing color tenability and possessing high quantum yield and high extinction coefficient. Although the investigation of II-VI have attained a mature level of understanding of the photo physical properties, suppression of the nonradiative decay channels and enhancing the optical properties for III-V material systems still remain a challenge. In this study, we have developed and demonstrated a simple, very fast, and efficient strategy to synthesize the highly luminescent III-V group based In(Zn)P quantum dots (QDs) utilized by the effect of core growth temperature, revealing their emission kinetics and their outstanding application for white light generation. Varying the core growth temperature from 240°C to 90°C, limiting the extent of the precursors involved in the synthesis, and a substantial enhancement of the photoluminescence quantum yield up to 75% is demonstrated. Further modification of the synthesis procedure with optimizing the In:P precursor ratio for the first time up to 88.5 ± 5.5% quantum yield of alloyed core/shell In(Zn)P/ZnS QDs is achieved, in which the whole synthesis process takes only around one hour. In addition, as a demonstration of Cd-free pellets, versatile pellets of green and orange emitting QDs within KCl macrocrystals are prepared. Hybridizing with blue LED, a white light with correlated color temperature of 4597K along with an unprecedentedly high color rendering index of 90 is presented
… Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) were performed using Thermo Scientific Nicolet-6700 and white LED characterizations were carried out using fiber coupled StellarNet Inc. Spectrometer and Konika Minolta LS150 Luminancemeter. 2.3 QD Synthesis methods …





